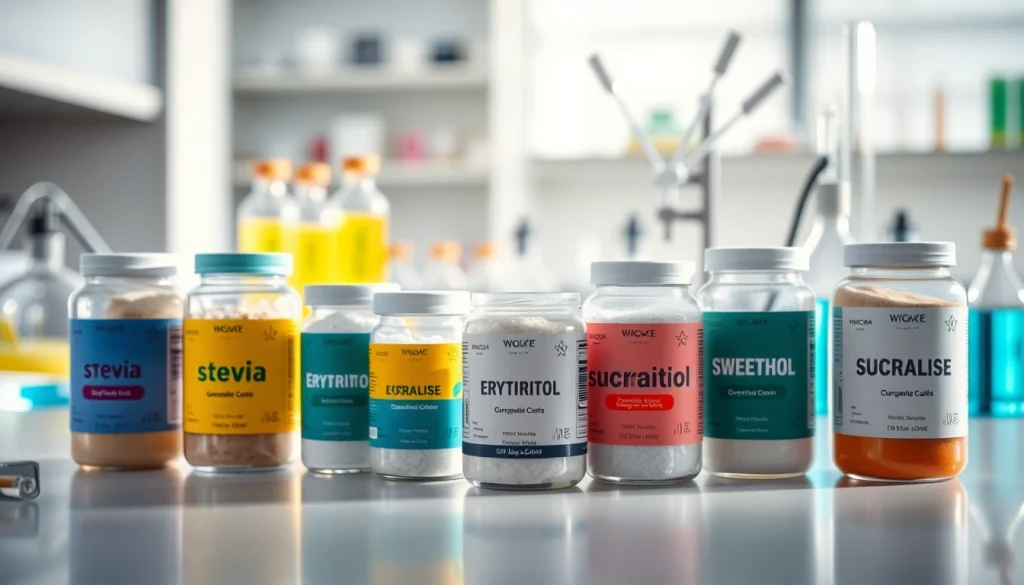
Introduction to Industrial Sweetener
The trend toward healthier lifestyles has led to a growing interest in industrial sweetener alternatives across various sectors, including food, beverage, and pharmaceuticals. While sugar has long been the standard sweetening agent, industrial sweeteners have emerged as a viable substitute, helping companies reduce caloric intake while maintaining desirable flavor profiles. This article explores the various facets of industrial sweeteners, their applications, benefits, and regulatory considerations.
Definition and Importance of Industrial Sweetener
Industrial sweeteners are substances used to impart sweetness in foods and beverages, often with lower caloric content than sugar. They can be derived from natural sources or synthesized through chemical processes. Their importance lies in their ability to meet consumer preferences for low-calorie or no-calorie options, cater to dietary restrictions, and enable food manufacturers to create products with enhanced shelf life and taste consistency.
Applications of Industrial Sweetener in Different Industries
Industrial sweeteners find extensive applications across various sectors. In the food industry, they are used in products ranging from beverages and baked goods to sauces and dairy products. In pharmaceuticals, they enhance the palatability of medicines, making treatments more appealing, particularly for children. The cosmetic industry also utilizes sweeteners in formulations for flavoring and soothing properties. Furthermore, their use in dietary supplements and health foods reflects a growing consumer demand for natural and health-conscious products.
Health Implications of Using Industrial Sweetener
While industrial sweeteners can provide benefits such as reducing sugar intake and managing weight, there are ongoing debates about their potential health implications. Some studies suggest that certain sweeteners may be linked to digestive issues or metabolic changes. Additionally, long-term consumption may lead to altered taste preferences, where consumers may exhibit a heightened desire for sweet flavors. Therefore, while they offer alternatives for sugar, it is essential to approach their use with an understanding of individual health needs.
Types of Industrial Sweetener
Natural Industrial Sweeteners: A Closer Look
Natural industrial sweeteners are derived from plants or other natural sources, making them appealing to health-conscious consumers. Examples include stevia, derived from the leaves of the Stevia rebaudiana plant, and monk fruit extract, which is several hundred times sweeter than sugar but contains no calories. These sweeteners often contain additional bioactive components that may benefit health, further enhancing their attractiveness in a market focused on whole foods and “clean” labels.
Synthetic Industrial Sweeteners: Pros and Cons
Synthetic or artificial sweeteners, such as aspartame, sucralose, and saccharin, are chemically manufactured to yield intense sweetness without calories. While they allow for significant calorie reduction, potential drawbacks include controversies regarding their safety and association with adverse health effects. Regulatory agencies generally regard these sweeteners as safe at established levels, but consumer perception and preference are shifting towards natural alternatives, affecting their market viability.
Comparing Popular Industrial Sweeteners
Comparison of various industrial sweeteners reveals significant differences in taste, sweetness intensity, and caloric content. For instance, while aspartame provides sweetness comparable to sugar, other sweeteners like erythritol and xylitol have a lower glycemic index. Each sweetener’s unique profile influences its function in specific applications, making it crucial for manufacturers to choose appropriate options based on intended usage and customer requirements.
Regulations and Standards for Industrial Sweetener
Global Regulations Impacting Industrial Sweetener
Industrial sweeteners are subject to strict regulations that vary by region. In the United States, the FDA oversees the approval of sweeteners and establishes guidelines for their safe use. Similarly, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) evaluates and regulates sweeteners in the European Union, ensuring that they meet specific safety standards before being released into the marketplace. Such regulations play a crucial role in determining which sweeteners can be marketed and consumed, impacting industry practices.
Quality Control Measures in Industrial Sweetener Production
Quality control is paramount in the production of industrial sweeteners to ensure consistency, safety, and compliance with regulations. Manufacturers employ rigorous testing throughout the production process, from raw materials to finished products. This includes testing for purity, microbiological safety, and sensory properties, which ensures that the final sweeteners meet or exceed industry standards while providing consumers with safe products.
Labeling and Safety Standards for Consumers
Clear labeling and adherence to safety standards are essential for consumer protection. Labels must accurately represent the ingredients and nutritional information of products containing industrial sweeteners. Moreover, the inclusion of relevant allergen information and potential side effects is critical to inform consumers adequately. This transparency fosters consumer trust and promotes informed dietary choices.
Market Trends in Industrial Sweetener
Growth Factors of the Industrial Sweetener Market
The market for industrial sweeteners is experiencing significant growth, driven by an increased demand for low-calorie and sugar-free products. Rising healthcare awareness about lifestyle-related diseases and an inclination towards healthier food options further fuel this trend. Additionally, product innovation, including new formulations and applications, attracts diverse consumer demographics, thus expanding the market base.
Challenges Facing the Industrial Sweetener Industry
Despite its growth prospects, the industrial sweetener industry faces challenges, such as consumer skepticism about artificial ingredients and regulatory hurdles in different regions. Additionally, the need for continuous research and development to create new sweeteners that meet consumer expectations poses financial and operational demands on manufacturers. Competing with natural sweeteners also requires significant marketing efforts to educate consumers about the benefits and safety of synthetic options.
Future Outlook and Emerging Trends
The future of the industrial sweetener market is likely to be shaped by trends towards personalization and sustainability. More consumers are seeking products tailored to their individual health goals and preferences. Moreover, as the sustainability of ingredients becomes increasingly relevant, manufacturers may focus on sourcing raw materials from environmentally responsible practices. Collaborative efforts between producers and consumers will play a crucial role in the evolution of sweeteners to align with contemporary dietary trends.
Frequently Asked Questions about Industrial Sweetener
What are the benefits of using industrial sweetener?
Industrial sweeteners offer lower-calorie alternatives to sugar, helping manage weight and lower sugar intake without sacrificing taste.
Are there any side effects of consuming industrial sweetener?
Some individuals may experience digestive issues or headaches. Long-term effects require more research, but moderation is advised.
How does industrial sweetener compare to sugar?
Industrial sweeteners are significantly sweeter than sugar and often calorie-free, making them a popular choice for reduced-calorie diets.
Can industrial sweetener be used in baking?
Yes, many industrial sweeteners can substitute sugar in baking, though adjustments may be needed for optimal results due to varying sweetness levels.
What’s the recommended daily intake of industrial sweetener?
There is no universal recommendation. However, it’s wise to consume industrial sweeteners in moderation to mitigate potential health risks.