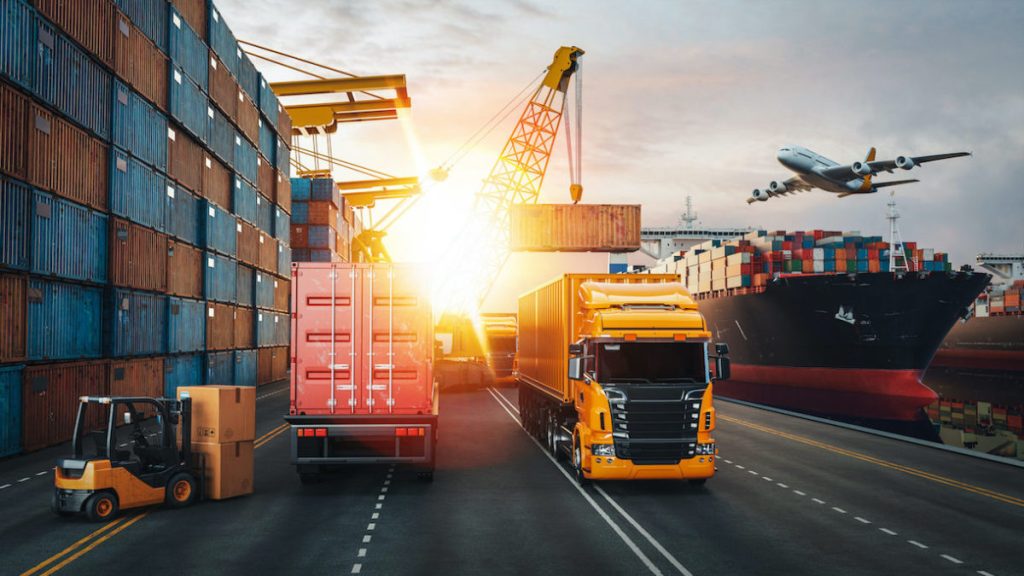
Introduction to Transportation
Transportation is a critical aspect of human activity that facilitates the movement of goods and people from one location to another. It includes various modes and systems, shaping not only our daily routines but also influencing economic development, urban planning, and societal interaction. Understanding the intricacies of transportation is vital in our fast-paced world, where efficiency and accessibility are paramount.
What is Transportation?
Transportation refers to the act of moving people, animals, and goods from one place to another using various means. This movement can encompass a variety of modes such as road, rail, air, and waterways. The core function of transportation is to connect individuals and communities while enabling commerce, enhancing productivity, and promoting tourism.
The Importance of Transportation in Daily Life
In our daily lives, transportation plays a significant role. It affects our ability to commute to work, access essential services, and engage in recreational activities. Efficient transportation systems can reduce travel time, increase access to jobs, and enhance overall quality of life. Moreover, robust transportation networks are essential for emergency services and disaster response, illustrating their critical role in safety and well-being.
Historical Overview of Transportation Systems
The history of transportation is woven into the fabric of human civilization. From ancient times, when people relied on walking and animal-drawn vehicles, to modern-day innovations such as electric vehicles and autonomous drones, transportation has evolved remarkably. Historical milestones include the development of the wheel, the establishment of roads and bridges in ancient empires, and the invention of the steam engine, which revolutionized transportation in the 19th century. The evolution continues today with the integration of technology, reshaping how we think about mobility.
Types of Transportation
Land Transportation: Buses, Cars, and Trains
Land transportation is primarily varied among three categories: personal vehicles, public transit systems, and freight transport. Personal vehicles, such as cars and motorcycles, offer flexibility and convenience. Public transportation, including buses and trains, serves larger populations and can alleviate traffic congestion by reducing the number of individual cars on the road.
Urban centers often rely on efficient railway networks and bus systems to provide comprehensive coverage and facilitate movement across cities. For example, cities like New York and London have extensive subway systems that enable quick, efficient transit for millions of commuters daily.
Air Transportation: Aircraft and Drones
Air transportation is pivotal for long-distance travel, allowing passengers and cargo to traverse vast distances in a short time. Commercial airlines operate scheduled flights, while charter services provide more flexible travel options. The advent of technology has also ushered in a new era of transportation with the rise of drones. Drones are now being used not only for recreational purposes but also in logistics, agriculture, and emergency deliveries, showcasing their immense potential in various sectors.
Water Transportation: Ships and Ferries
Water transportation continues to be a reliable method of moving large quantities of goods across seas and rivers. Container ships dominate the shipping industry, enabling global trade. Ferries facilitate short-distance travel across bodies of water, aiding in regional connectivity, especially in urban areas with considerable waterways. Notably, developments in eco-friendly vessels are underway, aiming to reduce the environmental footprint of marine transport.
Benefits of Efficient Transportation Systems
Economic Impact of Transportation
The transportation sector significantly contributes to the economy by creating jobs, enhancing productivity, and fostering trade. Efficient transport systems can lower costs for businesses, improve supply chains, and stimulate local economies. According to studies, every dollar invested in transportation infrastructure can yield up to four dollars in economic returns, making it a key area for public and private investment.
Environmental Benefits and Sustainability
As the world grapples with climate change, sustainability in transportation has become a priority. The transition to electric vehicles and the promotion of public transportation can reduce greenhouse gas emissions significantly. Countries are investing in green technologies such as hydrogen fuel cells and biofuels, while urban areas are developing cycling lanes and pedestrian-friendly infra-structures to encourage non-motorized forms of transport.
Enhancing Community Connectivity and Accessibility
Transportation systems play an essential role in connecting communities. Well-planned transit networks can provide access to healthcare, education, and employment opportunities. Furthermore, accessible transportation options for the elderly and disabled are crucial to ensure inclusivity in society. By enhancing connectivity, communities benefit from increased social cohesion and economic resilience.
Challenges in Transportation
Traffic Congestion and Urban Sprawl
One of the most pressing issues facing urban transportation is traffic congestion, often exacerbated by urban sprawl. As cities expand, public transport systems can struggle to keep pace, leading to increased reliance on personal vehicles and more traffic jams. Strategies to combat congestion include implementing congestion pricing, expanding public transit, and promoting alternative modes of transportation like cycling and walking.
Infrastructure Maintenance and Safety Concerns
Maintaining transportation infrastructure poses a significant challenge across the globe. Aging roads, bridges, and rail systems require continuous inspections and maintenance to ensure safety. Federal and state governments often face budget constraints that hinder adequate investment in infrastructure. Prioritizing funds, enhancing public-private partnerships, and utilizing technology for proactive maintenance can alleviate some concerns related to infrastructure safety and reliability.
The Role of Technology in Overcoming Challenges
Technology is becoming an integral part of modern transportation solutions. Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) use data analytics, real-time traffic monitoring, and smart routing to improve traffic flow and reduce congestion. Apps that provide route optimization, along with autonomous vehicle technology, promise significant advancements in safety and efficiency in the years to come.
The Future of Transportation
Innovations in Transportation Technology
The future of transportation is inextricably linked to technological progress. Innovations such as electric and autonomous vehicles signal a shift toward safer, cleaner transportation options. Additionally, the development of Hyperloop systems and flying cars captures the imagination for rapid transit systems that may one day redefine distance and accessibility in urban settings.
Trends in Sustainable Transportation Solutions
To combat climate change, sustainable transportation solutions are more crucial than ever. Trends towards shared mobility, such as car-sharing, ride-sharing, and bike-sharing services, reduce the number of vehicles on the road. Governments are also increasing investments in public transit, non-motorized transportation infrastructure, and clean energy advancements to foster a more sustainable future.
Government Policies Shaping the Future of Transportation
As transportation continues to evolve, government policies will play a pivotal role in shaping the future landscape. Regulations promoting electric vehicle adoption, improvements in public transit systems, and funding for infrastructure upgrades are essential components of effective transportation policy. Collaboration between various stakeholders, including government agencies, private companies, and community organizations, will be vital to aligning goals and achieving sustainable outcomes.